Binding
A binding is a continuous connection between two values. If two objects are connected with a binding each time a value changes in one object then the updated changed value is propagated to the other object.
Binding is a very powerful concept in software development. Creo offers an intuitive way to create bindings between objects visually by using the Binding knob anchor point:
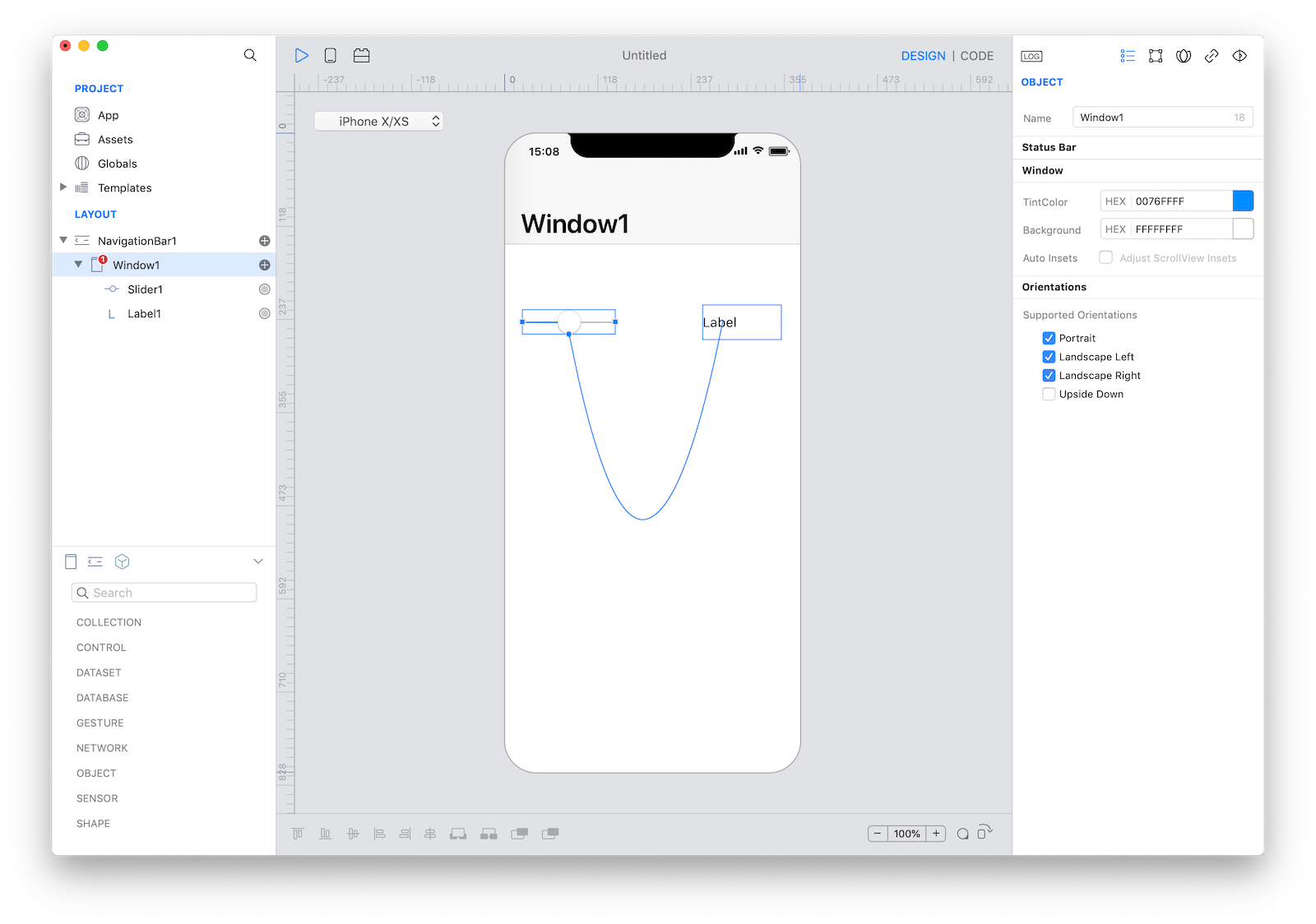
Once two objects are connected then you can configure the Binding using its Inspector:
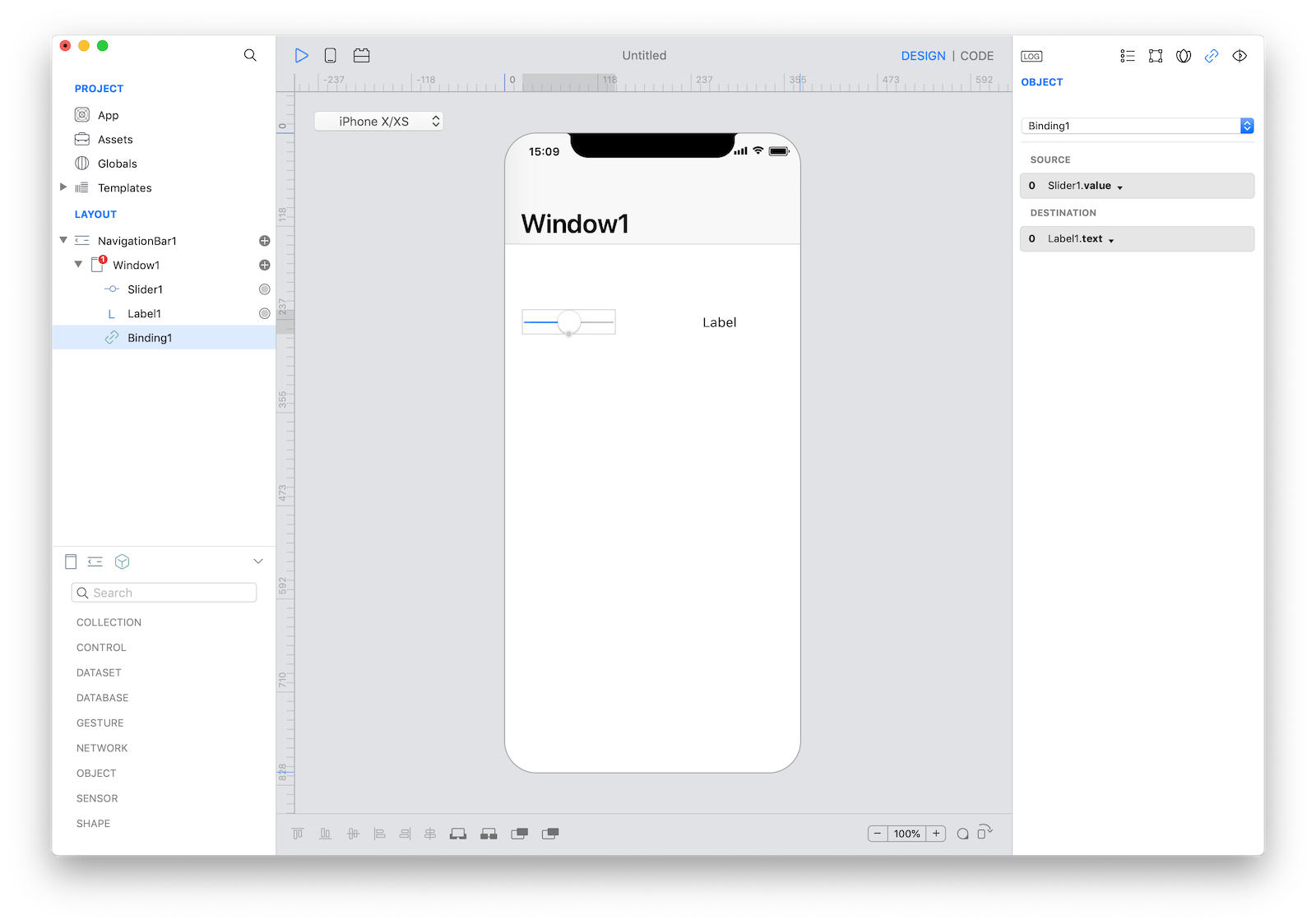 In the example above the value of the Slider1.value property is continuously connected to the Label1.text property. Bindings are listed in the Layout pane that you can be selected and customized.
In the example above the value of the Slider1.value property is continuously connected to the Label1.text property. Bindings are listed in the Layout pane that you can be selected and customized.
Advanced Binding
Creo offers fleible bindings enabling you to connect more than one object in a single binding. Suppose for example that you'd like to add to the user the ability to create a new Color, a Color is a class that can be instantiated using an RGB value.
Start by dragging 3 Sliders and a View into the Design Board:
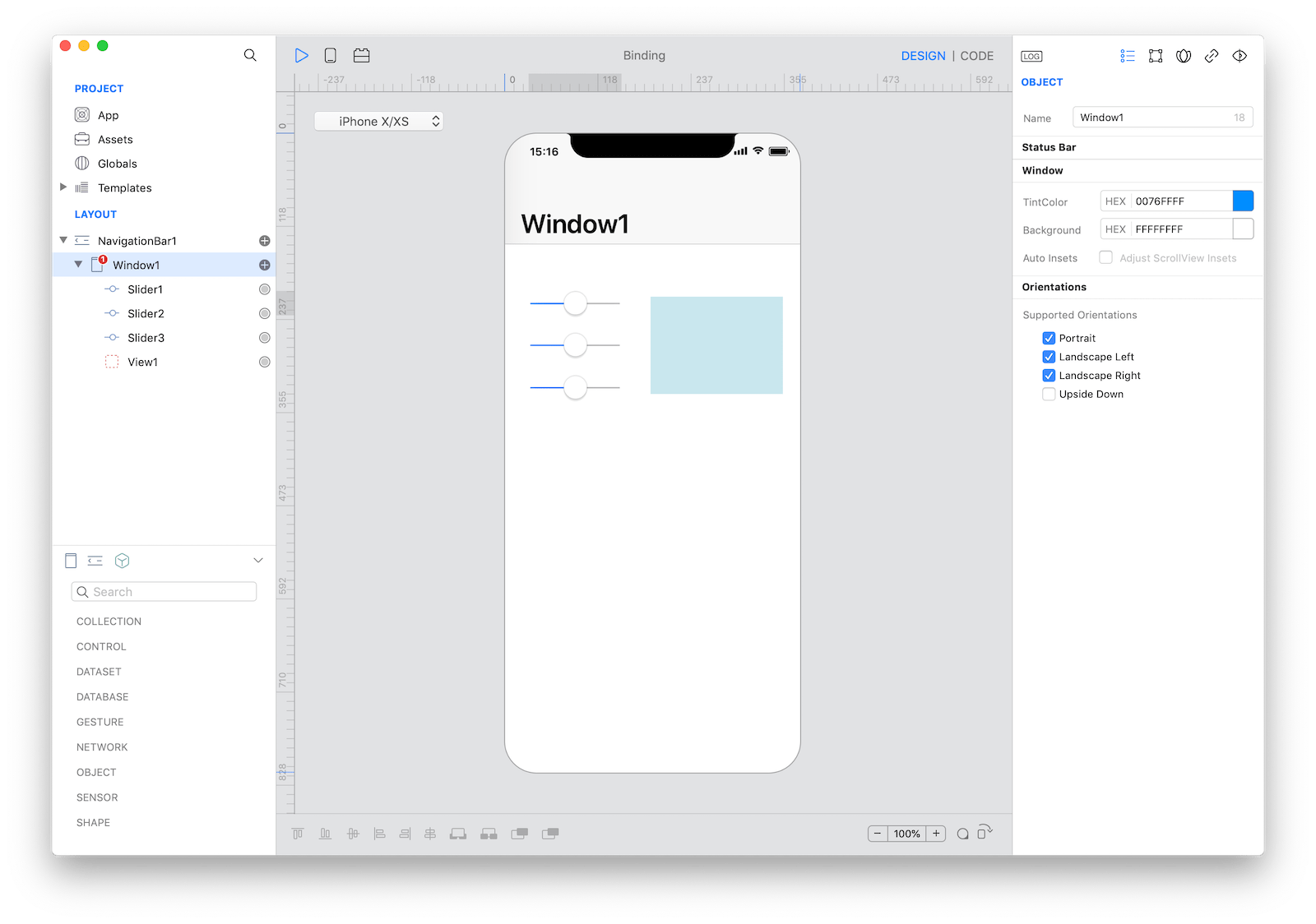
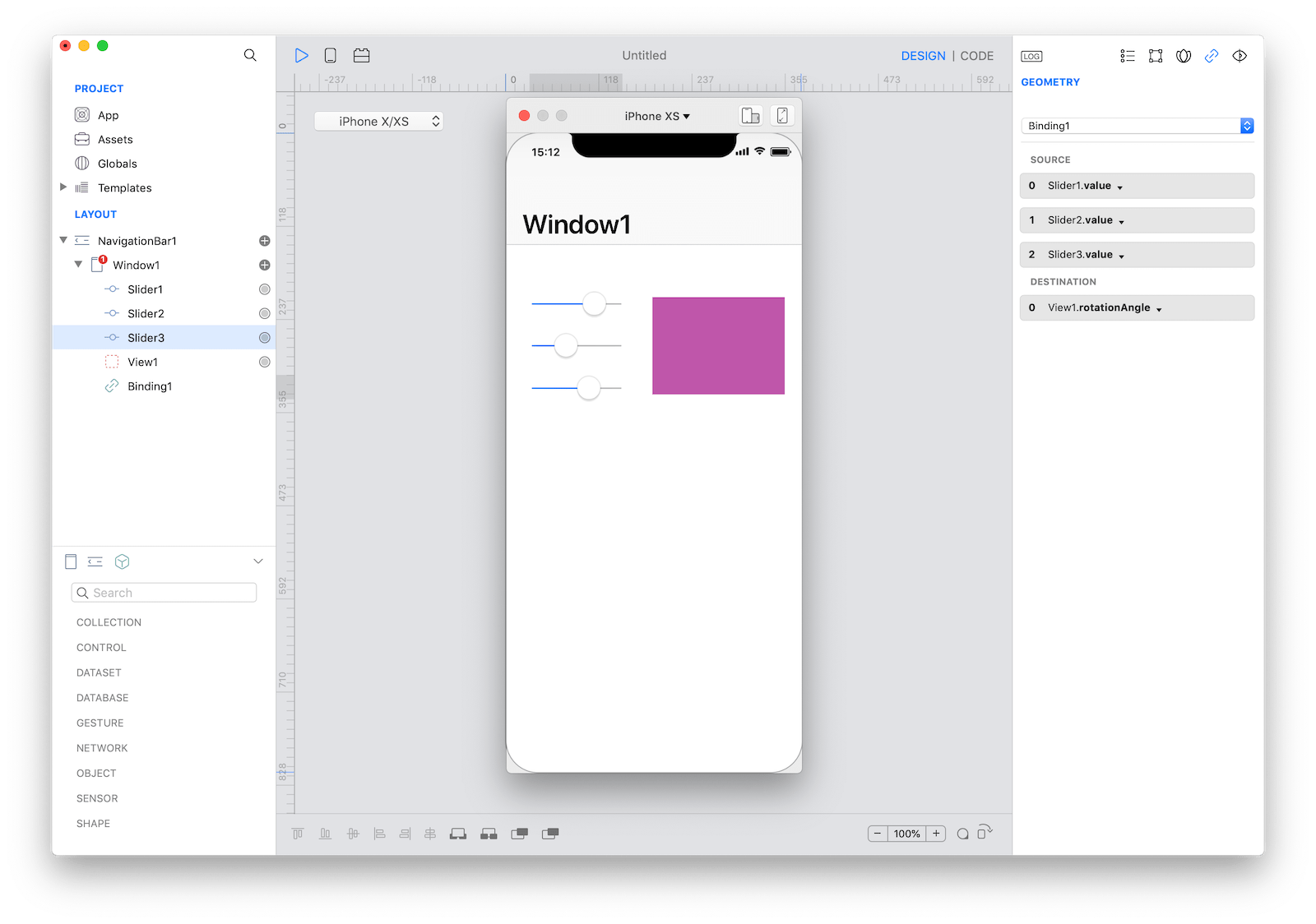
Create a binding between Slider1.value and View1.backgroundColor and then add Slider2.value and Slider3.value to the same Binding:
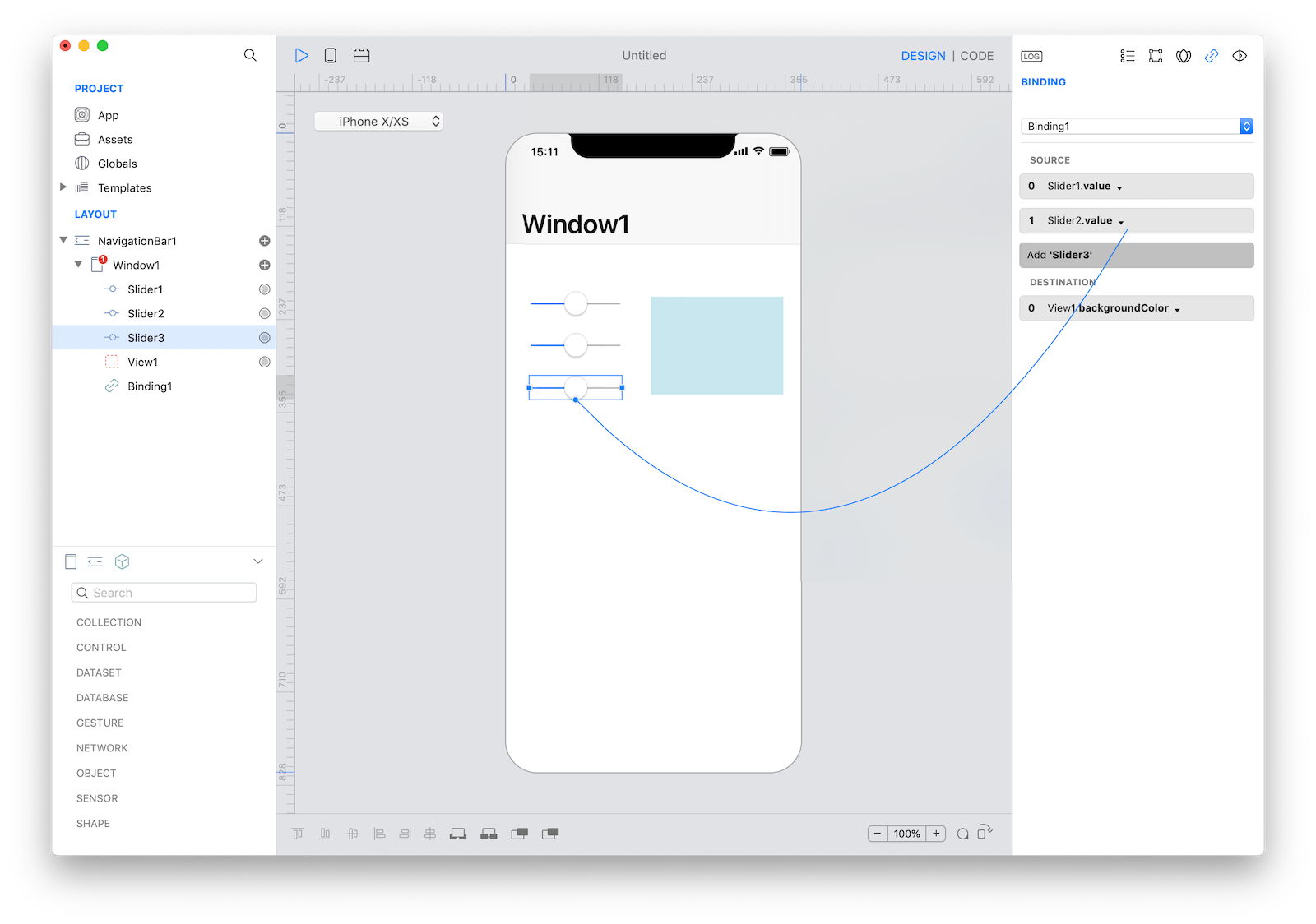
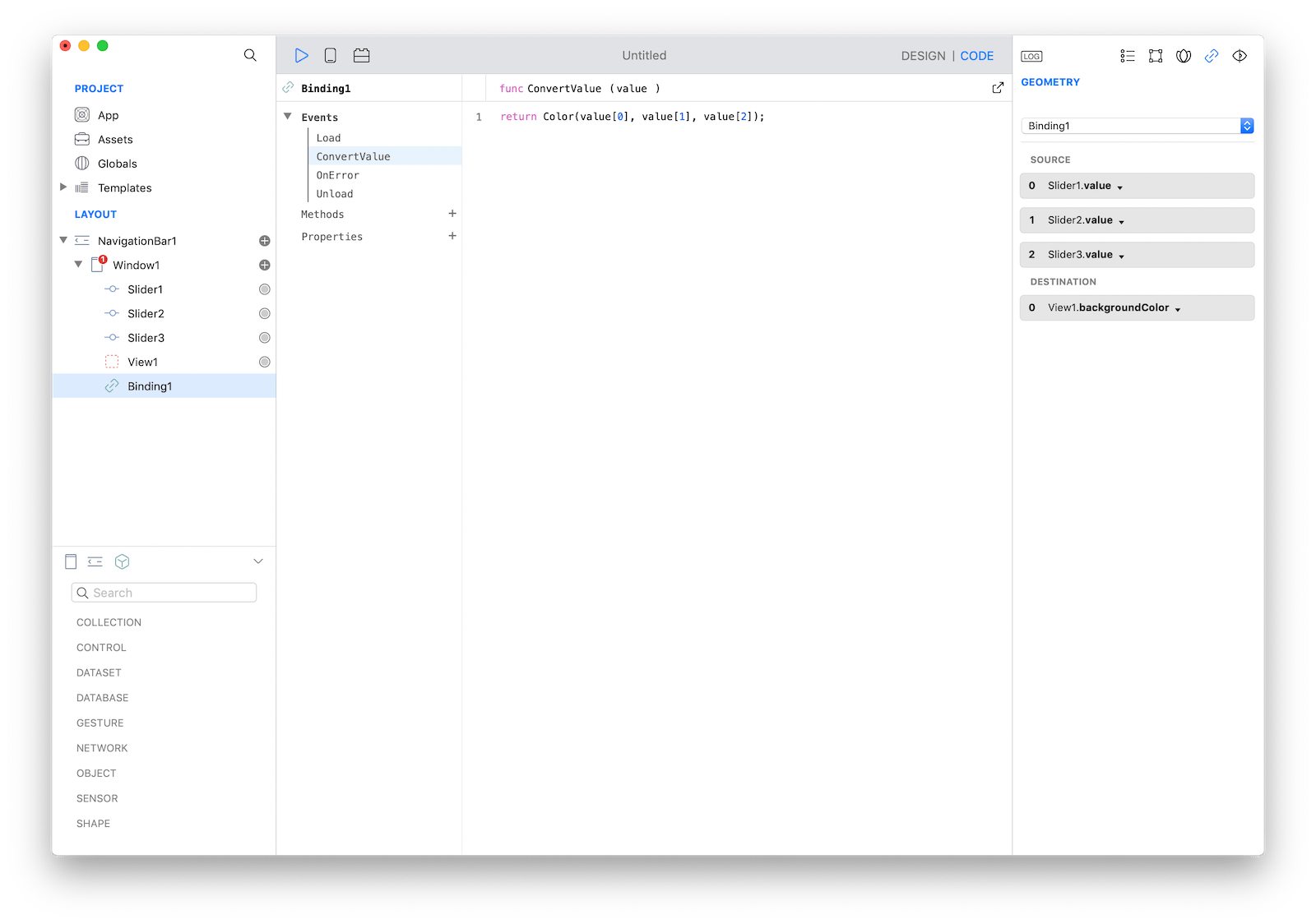
Select Binding1 on the Layout pane and open the SourceConversion event. This event is called each time the binding needs to send a value from source objects to the destination object. The value parameter represents a single value when there is only one SOURCE object, while it is an array of value when objects in the SOURCE group are more than once.
The resulting value is expected to be a Color (because the destination property is View1.backgroundColor) and if you read documentation about the Color class (under the INITIALIZERS section) you can see that a way to create a new Color is just to instantiate the class passing 3 float parameters (which represent the Red, Green and Blue value). All of this can be done with a single line of code:
Pess Run to see your app running into the Creo Simulator: